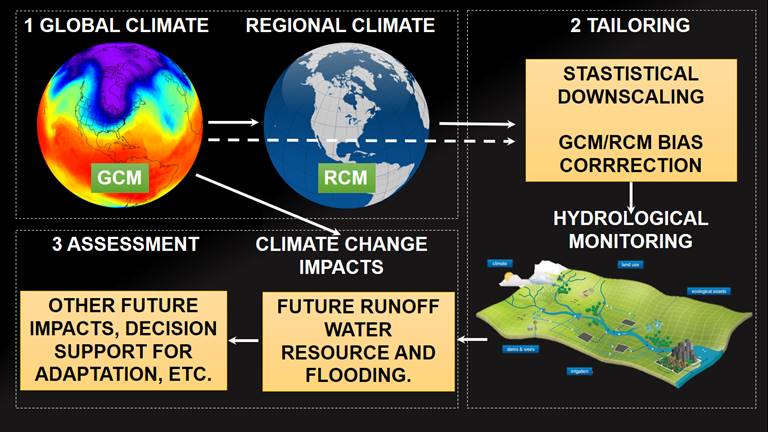
Climate change significantly influences the precipitation pattern of the Area of Impact (AOI) for Solar Power Plants. This influence eventually poses risks to the power generation, inadequacy of the generating assets and damage to the associated infrastructure of the project.
Hydrological Risk Assessment being a critical component of solar power plant design, involves the identification of potential hazards and design mitigation strategies. Considering Climate Change scenarios during hydrological risk assessment for solar power is highly important due to the following reasons: –
1. Changes in precipitation levels can lead to water unavailability and increased runoff. Design of water storage and drainage systems for solar PV system needs to be reviewed and vetted beforehand to ensure resilience. It may lead to more intense and frequent rainfall events.
Higher precipitation intensity can overwhelm drainage systems and increase the risk of localized flooding. Climate change can also cause shifts in the distribution of rainfall, affecting the timing and geographic patterns of precipitation. This can lead to changes in river flow regimes and impact flood risk in different regions. Incorporating these changes in the flood risk assessments helps identify areas prone to increased or decreased flood risk. The flood risk assessment must consider these changes in precipitation patterns to accurately assess the likelihood and severity of flooding.
2. Changes in temperature can lead to changes in evaporation rates, and streamflow. This can impact the design of water management systems for solar power plants.
3. Increased frequency and severity of extreme weather events: Climate change may cause an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events such as floods and droughts. This can impact the design of flood and drought mitigation strategies for solar power plants.
4. Sea-level rise: Sea-level rise caused by climate change can impact coastal solar power plants by increasing the risk of flooding and saltwater intrusion into freshwater resources.
5. Changes in water quality: Climate change can impact water quality, which can affect the performance and lifespan of solar panels. Increased water temperature and changes in nutrients can impact the module cleaning process.
To suggest efficient mitigation measures, it is important to consider the potential impact of climate change on hydrological systems and accordingly design solar power plants that are resilient to these changes. This can be done by incorporating climate projections into the design and operation of solar power plants and developing robust water management and flood mitigation strategies.